Cuba is a great historical, cultural and natural patrimony. It doesn’t a surprise that many places are included in the list of the Heritage of UNESCO and also protected Reserve of the Biosphere. We visit up to 10 places of this list during our trip programs: Pearl of the Caribbean and Beach and Sightseeing
Contents
Patrimonial tourism is based on the active experience of the place through which we discover the riches of the region; we know their inhabitants, we have the opportunity to see the singularity of the natural and cultural patrimony and the beauty of the landscapes. It allows us to be near people, their traditions, culture and local nature, and in an ideal situation, the residents are aware of the beauty of the region, they give an impulse to develop the managerial spirit and they also facilitate the construction of the local identity and the cooperation. This is our dream of travelling consciously to Cuba and we make an effort to achieve it on each trip.
This type of trip even has its name: patrimonial tourism. It is to travel to know places, objects of material and spiritual culture, as well as activities that present the genuine history and the cultural values, passed already as well as presents. Nowadays, like part of the education, before travelling to Cuba (although probably for many people right after), we present places of the extensive list of the UNESCO. In the first list, we introduce the tangible patrimony, followed by the reserves of the biosphere and then intangible patrimony. Do you see it? There is really a lot! Cuba has great wealth!
Objects of the list of World Heritage of UNESCO in Cuba
- Historical Complex in Havana and its fortification system (1982)
- Trinidad (1988)
- Sugar Mill Valley (1988)
- The Valley of Vinales (1999)
- Cienfuegos (2005)
- Camagüey (2008)
- Castle of San Pedro of the Rock (1997)
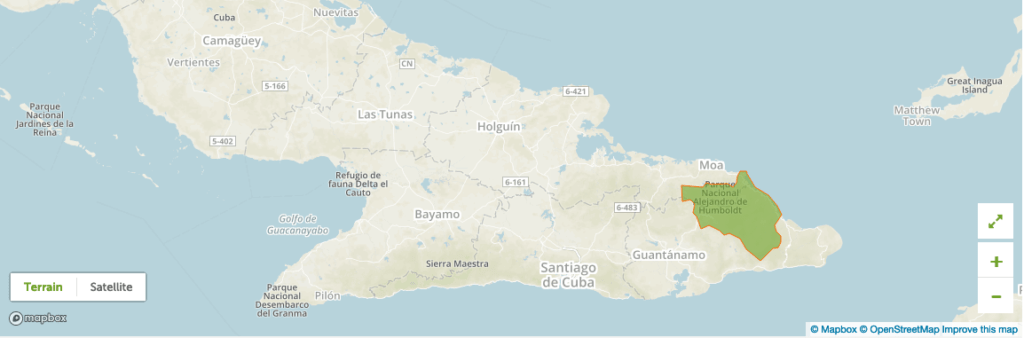
- National Park Alexander Von Humboldt (2001)
- National Park Landing of the Granma (1999)
- Archaeological Landscape of the first plantations of coffee in the southeast of Cuba (2000)
- Arch Cathedral of the Immaculate Concepción of Virgin Maria in Havana
Reserves of the biosphere of the UNESCO in Cuba
The Reserves of the Biosphere are designated protected areas that contain valuable natural resources. The Reserves of the Biosphere of the world were created as part of the activities of, among others, UNESCO. The nature of Cuba cannot be underestimated here. Then we have six areas included in the list of the Reserves of the Biosphere in Cuba! Here they are, together with the dates that were added to the list:
1984: Reserve of the Biosphere the Rosario Mountain range (1984)
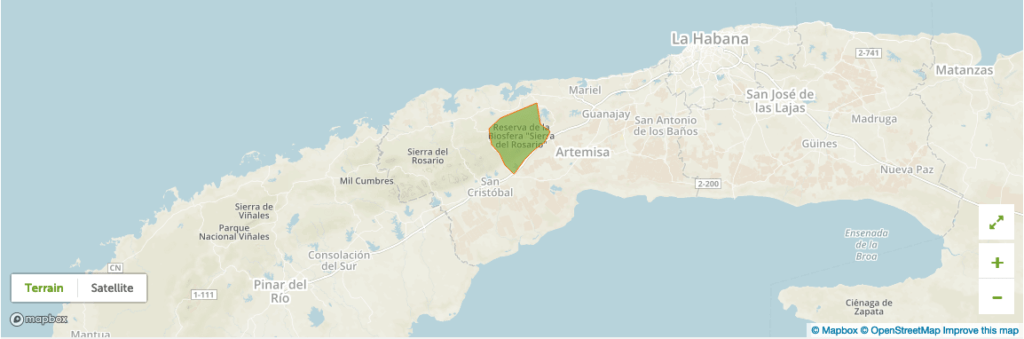
The Reserve of the Biosphere the Rosario Mountain range is located in the oriental part of the Guaniguanico’s Mountain range, between the provinces of Pinar del Rio and Havana, where it can be seen on both coasts, north and south. It covers an area of 26,686 hectares.
The reserve has a complex geologic structure with a great variety of rocks that produce different and special soils that determine the endemism of the flora through the landscape.
It is here where you can find the small purple orchid Bletia purpurea, considered the symbol of this reserve.
Some parts of the Reserve are covered with serpentine rock, and instead of a forest, there are grasslands and brushwood as well as xeromorphic bushes. Still, with intact special characteristics, natural systems in regeneration and an ecological field station, the Rosario Mountain range has been cleaned out from the natural forest hull, but we still find semiprecious forests, hills, antlers, it is to say, atypical solitary values and secondary species of renewable forests, such as the royal palm and yagruma.”
More than 5.500 people live in this Reserve of the Biosphere and they have jobs link mainly to crafts, agriculture, animal husbandry and afforestation. Also, 62 national and 20 foreign scientists (1998) are involved in the investigation and monitoring in the Institute of Ecology and Systematic. They improved the tropical afforestation and agriculture, the local Ecotechnology, through the development of biofertilizers that contain diverse mixtures of micro enzymes. They also promote the use of non-conventional energy. Besides, there is a strong focus in the ecological education of the society and specialized eco-tourism. A very good ecological hotel: Mocha was built in the Reserve of the Biosphere that melts with the hillside.
Maybe one of the most interesting aspects of the Reserve of the Biosphere is its relation with coffee. It was the place of the first big plantation of the New World, and there are several places in the Reserve where exist small independent farms, and the shady coffee is part of the range of cultivated products. In Buena Vista, there is a great area to dry coffee, where the techniques and machines of the XIX century are still extremely well conserved. In combination with the Reserve of Biosphere of Mazatlan Mountain range in Mexico, it shares similar environmental conditions but also problems of resources administration.
Reserve of the Biosphere Knives of the Toa (1987)
The Reserve of the Biosphere Knives of the Toa is located in the biggest Antilles, northeast of Cuba, and it includes the mountainous region Sagua-Baracoa in the National Park Alexander Von Humboldt. It covers an area of 208 305 hectares, of which 6 013 belong to the area of the sea.
Knives of the Toa is considered one of the main centres of biodiversity and endemism in Cuba and the Caribbean Islands, with mountain forests, cloudy forests, until the complex coastal vegetation with mangrove swamps and coral reefs. The karst system of the great cave of Moa Head is one of the five natural monuments of the country and one of the biggest cave systems of the east of Cuba.
With a high flora and fauna biodiversity, 928 endemic species, such as the gender Podocarpus and Dracaena, botanical gems belonging to the most primitive species are observed. The presence of vertebrates like the Ivory-billed Woodpecker (Campephilus principalis), the Cuban Kite (Chondrohierax Wilson) and the almiqui (Solenodon Cubans); is also considered very much in danger of extinction. Some of the smallest species of mammals in the world can be found in the Reserve.
About 18 300 inhabitants (2002) live in the Reserve, split out into 498 communities. They are involved in forestry, traditional agriculture (coffee, coconut and cocoa) and ecotourism. They raise cattle and participate in the searching of nickel, chromium, iron and cobalt. These activities had a bigger negative impact on the capacity of the ecosystems that is one of the main problems that face the reserve nowadays.
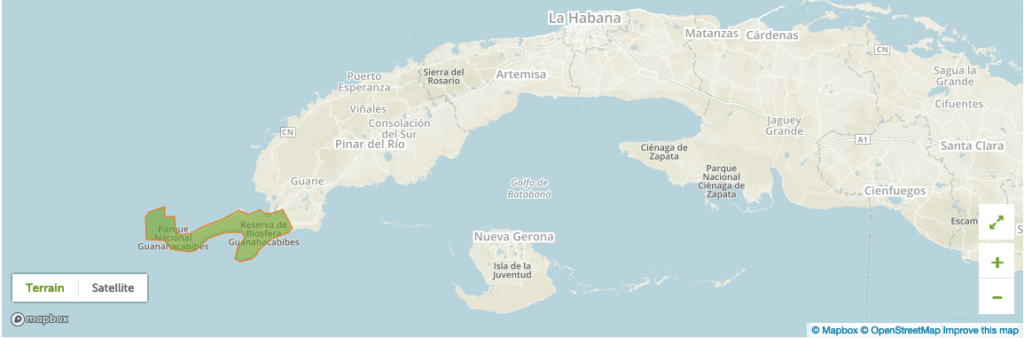
The Peninsula of Guanahacabibes (1987)
It has the reservoir of the most western biosphere with the famous diving centre María la Gorda in the province of Pinar del Rio. The Reserve has more than 100 lakes that, like wetlands, are separate it from the Cuban continent. The Reserve has also the biggest and cleanest fields of quartz sand with a purity of 99.8%.
Due to this difficult access, the Spaniards didn’t get here, and the area was ahead of the bridge of the native aboriginal population. So far, there are 140 archaeological sites related to the life of Guanahatabeyes, because this is the population’s name that used to live in these areas.
Guanahacabibes is a paradise for bird watching but there are also strange species of reptiles and amphibians. The experts also believe that 4 of the 7 species of marine turtles that live on the planet survived in the Guanahacabibes Peninsula. The nature tourism is the main attraction of the National Park with an area of 398.26 km2. This area is inhabited by 172 species of birds belonging to 42 families, from which 11 of those are endemic and 84 migrate. The coast also contains very well preserved coral reefs.
The most western place in Cuba is the San Antonio cape. Guanahacabibes was the place of the first field of forced works of Cuba that began at the end of the decade of 1960.
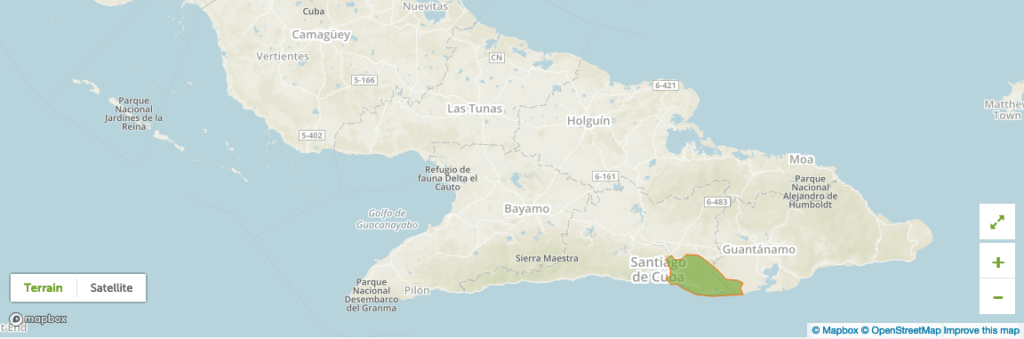
Reserve of the Biosphere ‟Baconao” (1987)
The Reserve of the Biosphere of Baconao is located in the provinces closer to the tropic, to the southeast of Cuba, between Santiago de Cuba and Guantánamo that it includes three bio-geographic areas very well defined: “Upland of Santiago”, the “Great Stone Mountain range” and the “Santa Maria of Loreto Upland”.
The Reserve includes rainy forests, cloudy forests, a forest of the mesophilic foot of perennial leaf and microfilaments of perennial leaf, coastal and sub coastal xeromorphic bushes with forests of pines and columnar cactus. The rocky and sandy coastal habitats, the mangrove swamps and the ecosystems of caves are considered other important habitats. High flora biodiversity (1.800 species notified) and fauna and many endemic species in danger of extinction have been reported such as bats, spiders and species of insects that live in natural caves (46.6% of the ornithofauna).
The Reserve has 38,000 inhabitants (2001) that work in tourism, forestry, cattle raising and agricultural ecosystems with coffee, fruits and ornamental flowers. Annually, the reserve is visited by approximately 96,360 national tourists and 275,366 foreigners. Almost 90% of the population has this activity thanks to 13 centres of tourist lodging, a museum and 3 camping sites that are in the area of the reserve.
One of the most interesting aspects of the reserve of the biosphere is the important archaeological site that designated three old native cultures: ‘ Siboney’, ‘ Protoagricultor’ and ‘agriculture. This was the place of the coffee plantations of old immigrants (Haitian and French) that also influenced the local costume of the introduction of species of plants with medicinal, nutritious and ornamental destine.
There are 270 permanent investigators and 80 foreign investigators who participated in activities of investigation and monitoring administered by the Ministry of Science, Technology and Environment in Cuba (CITMA) in several laboratories of investigation and monitor in this area. The most important of them it is the “Oriental Center of Ecosystems and Biodiversity” (BIOECO).
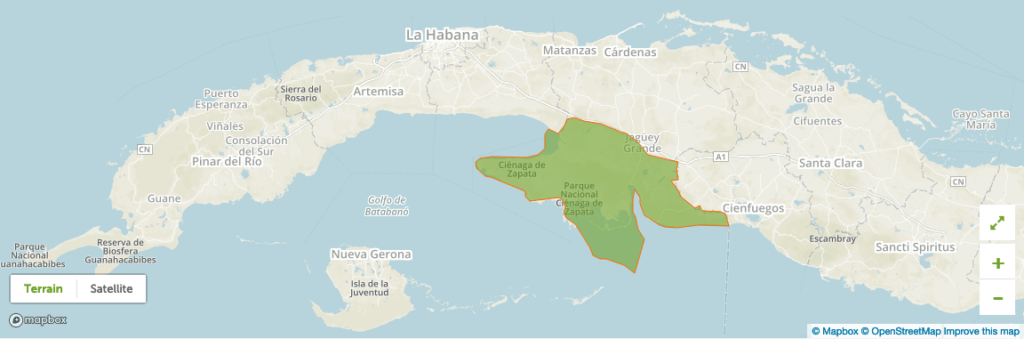
Reserve of the Biosphere Zapata Swamp (2000)
The Reserve of the Biosphere Zapata Swamp is located to the south coast of Cuba in the province of Matanzas and it covers an area of 628.171 hectares. It is one of the biggest and most important swamps of the Caribbean with a south marine frontier. This area is a reserve of the biosphere in a cluster with several basic areas, very valuable for the conservation, located in the National Park Marsh of Zapata.
This reserve shows the great diversity of ecosystems and types of coverage of the earth, such as grasslands, mangrove swamps, forests of marsh and semi-leaves, coastal and sub coastal forests of the perennial leaf; coastal and sub coastal heaths and coral reefs with the main species of corals and coastal lagoons.
This area is also the place where live the Cuban crocodile (Crocodylus hombifer) and the American crocodile (Crocodylus acutus) and birds, including the Greater Flamingo (Phoenicopterus rubber).
Around 9,000 people, mainly Spanish descendants, live in the Reserve. The economic activity includes mainly forestry, fishing, social agriculture, tourism, craft and beekeeping. Tourism in the Swamp Reserve is very important and it attracts more than 800,000 people every year, in benefit of the local communities. The region of the Reserve of the Biosphere Zapata Swamp has been declared a special region for sustainable development. This reserve is connected to the National Reserve of Biosphere of the Lizard River in Mexico.
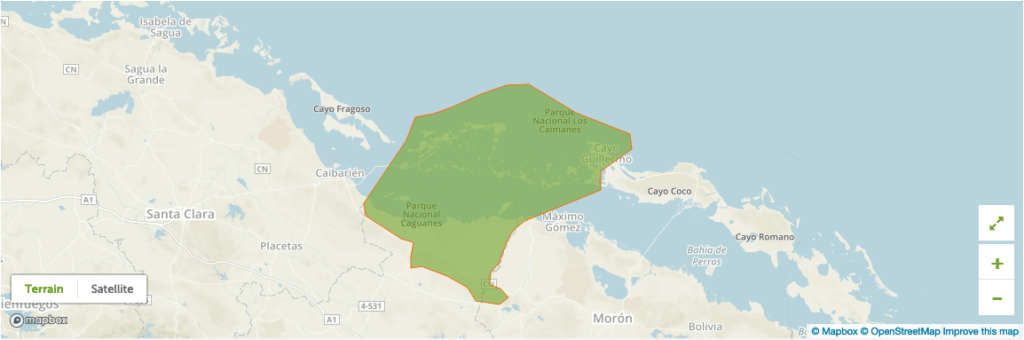
Reserve of the Biosphere of Buena Vista (2000)
The Reserve of the Biosphere of Buena Vista is located to the north coast of Cuba, in some parts of the provinces of Villa Clara, Sancti Spiritus and Ciego of Ávila, with a total area of 313 502 hectares. The biggest part of the sea includes coral reefs, rocky and sandy beaches, while the part of the ground it consists on a coastal forest of microfilaments of perennial leaf, mangrove swamp and heath.
The area has a high flora and fauna biodiversity and many endemic species (20), many of them in danger of extinction. The Reserve of the Biosphere of Buena Vista covers eleven main areas divided into two National Parks: Caguanes and Key Santa Maria-Key the Witches. These areas of keys contain extraordinary natural, historical and cultural values with 35 archaeological places and caves with rural art and mural paintings.
About 25.524 permanent residents (2001) live in the Reserve of the Biosphere in four cities and six rural villages. Their main economic activities are tourism, craft, traditional medicine, beekeeping, traditional agriculture (sugarcane), fishing, forestry and local agriculture. Tourism has the potential of development very significant.
To maintain the traditional practices of using the natural resources by the local communities strengthen their cultural identity. Many programs of environmental education are implementing in the reserve of the biosphere. They have carried out several national and international scientific projects as well as activities of investigation that are in course, including hydrometeorological parameters, protection of beaches, as well as characteristics and possible exploitation of water and mud in small islands. The UNESCO offers support for the project of investigation of mangrove swamps. The reserve is a twin of the National Reserve of Biosphere Contoy Island in Mexico.
Elements of the list of the Immaterial Cultural Heritage of the UNESCO in Cuba:
French Tumba
It is an Afro-Cuban secular gender of dance, singing and percussion that was originated in Cuba in the oriental province. Tumba was presented by slaves from Haiti that was a well-known French colony known as Saint-Domingo, whose proprietors settled down in the oriental regions of Cuba after the revolt of slaves in the decade of 1890. The rhythm flourished at the end of the XIX century with the creation of societies of French Tumba (associations of French Tumba), from which only three survived (Mason, Yubá, Frenté).
Cuban Rumba
Rumba comes from Cuba, but it doesn’t have anything to do with sociable people. The slaves began to dance after the slavery… abolition of slavery (1886). When they began to move to cities and towns from old work fields, naturally appeared collective events called rumba. Later on, the instruments appeared, and the first of them was a box in which cod was cared, due to the excellent quality of the wood that was famous for its acoustics.
Cuban Point (Punto)
Peasant point or Cuban point, or simply point, is a sung gender of Cuban music, poetic art with music. It became popular in the western and central regions of Cuba in the XVII century and as a gender strengthened in the XVIII century. It comes from Andalusia and the Canarias Islands and there were integrated African elements in Cuba.
Point is interpreted by a group with different types of guitars: Spanish, Cuban, French and three. Point refers to the use of a pick (dotting) and not to a beating (raking). There are three percussion instruments: clave, guiro and Guayo (also to grate, but metal made). The singers form bands and improvise their lines. They sing an unalterable melody with pauses among lyrics to give time to the singers to prepare the following verse.
The Sprees of Remedios (Remedies)
The tradition began on December 25 to incentive the slept Cubans in the church. The priest gave the children spoons and pots and he told them to run along with the city and to play the more lauder possible to wake up to the faithful ones. The effect was achieved: the Cubans appeared in the church by curiosity. The Sprees still work like a great carnival party that begins the first days of December and it lasts until January or more.
Here there are 10 places that we visit during the tours Hola Cuba – Perla del Caribe and Beach and tourist visits:
- Reserve of the Biosphere Zapata Swamp (Bay of Pigs)
- The Valley of Vinales (Valley of Vinales)
- Reserve of the Biosphere Rosario Mountain range (Soroa)
- Historical complex in Havana
- The fortification system of Havana
- Arch Cathedral of the Immaculate Concepción of Virgin Maria in Havana
- Trinidad
- Sugar Mill Valley (Sugar Mill Valley)
- The historical centre of Cienfuegos
- Reserve of the Biosphere of Buena Vista (Key Santa Maria)